代码
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 准备数据
x = torch.linspace(0, 100, steps=100).type(torch.FloatTensor)
rand = torch.randn(100) * 10
y = x + rand
x_train = x[:-10]
x_test = x[-10:]
y_train = y[:-10]
y_test = y[-10:]
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
plt.plot(x_train.data.numpy(), y_train.data.numpy(), 'o')
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('Y')
plt.show()
# 训练
a = torch.rand(1, requires_grad=True)
b = torch.rand(1, requires_grad=True)
learning_rate = 0.0001
for i in range(1000):
preditions = a.expand_as(x_train) * x_train + b.expand_as(x_train)
loss = torch.mean((preditions - y_train)**2)
print("loss:", loss)
loss.backward()
a.data.add_(-learning_rate*a.grad.data)
b.data.add_(-learning_rate*b.grad.data)
a.grad.data.zero_()
b.grad.data.zero_()
x_data = x_train.data.numpy()
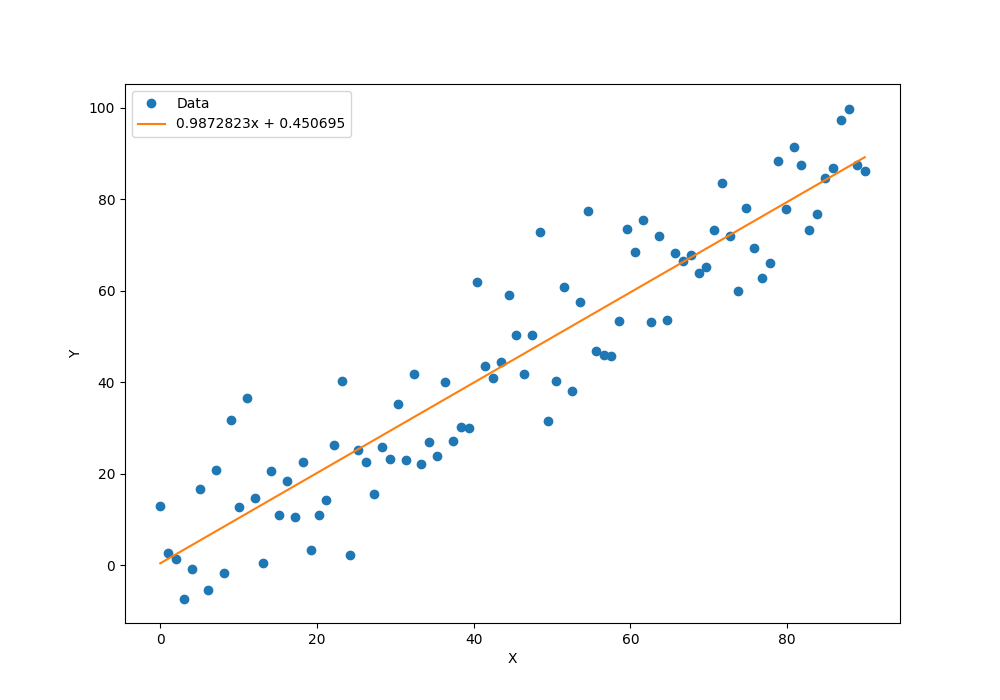
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 7))
xplot, = plt.plot(x_data, y_train.data.numpy(), 'o')
yplot, = plt.plot(x_data, a.data.numpy() * x_data + b.data.numpy())
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('Y')
str1 = str(a.data.numpy()[0]) + 'x + ' + str(b.data.numpy()[0])
plt.legend([xplot, yplot], ['Data', str1])
plt.show()
preditions = a.expand_as(x_test) * x_test + b.expand_as(x_test)
print(preditions)
# 预测
x_data = x_train.data.numpy()
x_pred = x_test.data.numpy()
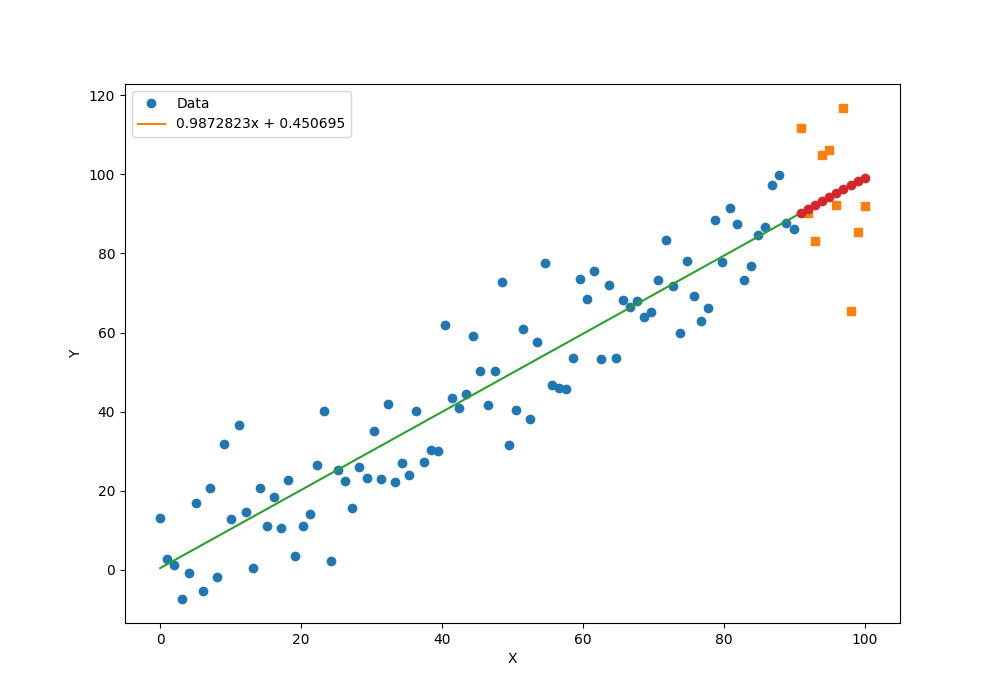
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 7))
plt.plot(x_data, y_train.data.numpy(), 'o')
plt.plot(x_pred, y_test.data.numpy(), 's')
x_data = np.r_[x_data, x_test.data.numpy()]
plt.plot(x_data, a.data.numpy() * x_data + b.data.numpy())
plt.plot(x_pred, a.data.numpy() * x_pred + b.data.numpy(), 'o')
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('Y')
str1 = str(a.data.numpy()[0]) + 'x + ' + str(b.data.numpy()[0])
plt.legend([xplot, yplot], ['Data', str1])
plt.show()
执行结果